Is this now really ‘the end’ of cash?

Below you will find an interesting article about the current state of cash around the globe, written by our employee Jan Heinvirta. He shares some very well supported arguments on whether COVID-19 means the end of cash.
Time and time again, people are predicting the end of cash. If you scrolled through LinkedIn recently, you might have seen several articles suggesting why this time it is for real. The reason? COVID-19. So let’s explore together the current state of cash around the globe to get a sense of whether this statement is valid.
E-Commerce experiences massive growth and fuels digital payment adoption
The ongoing pandemic has pushed many people and businesses to adopt digital solutions if they had not done so until today. E-commerce, for example, has seen incredible growth during the last months. New stores created on the Shopify platform surged 62% between March 13, 2020 and April 24, 2020, compared to the prior six weeks (1). In the U.S., e-commerce sales grew 14.5% in Q1 2020 compared to the same period in 2019, even though this only captures approximately two weeks of the full effect of the pandemic on U.S. retail. (2). Swiss farm-to-home delivery service Farmy mentioned an increase in demand of approximately 450% in dry products for pantry storage and around 300% in other categories (3). Mexican grocery delivery service Jüsto experienced a growth of 330% in orders and users already mid-March 2020 (4) when Mexico was still not as affected by the crisis compared to European countries like Italy or Germany judging by the number of confirmed cases (5, 6).
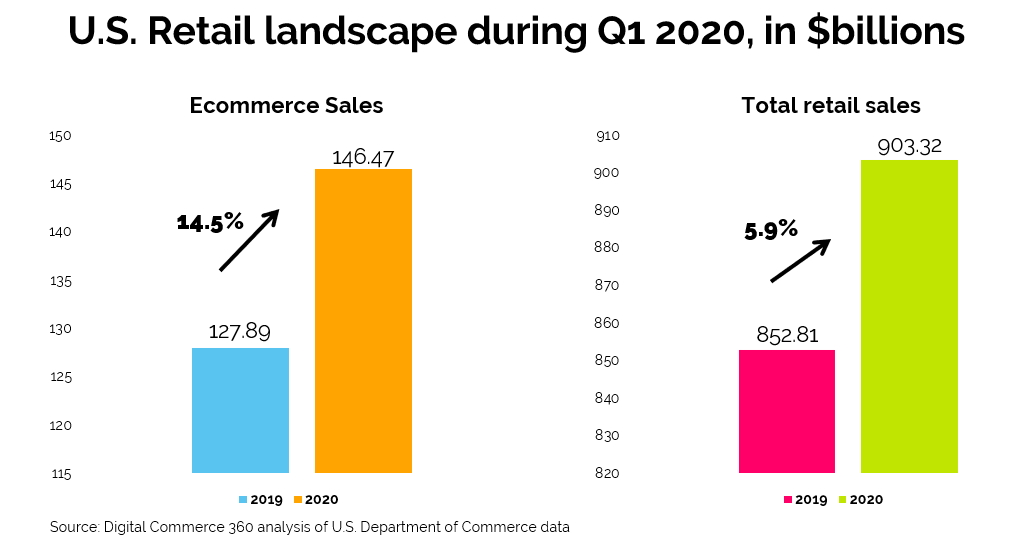
Simultaneously, this is also one of the factors that have led to an increase in electronic payments as most of the e-commerce transactions are paid digitally. I am specifically mentioning most since in markets like Mexico it is quite common that e-commerce transactions are paid in cash. J.P. Morgan‘s 2019 Payments Trends revealed that cash shares the spot as the second-most used e-commerce payment method next to mobile wallets, each taking a 17% share of the Mexican e-commerce payment market (7). Admittedly, these numbers must have seen quite a change during the pandemic. But an increase in e-commerce was not the only reason for the growth in electronic payments.
The myth around cash being a transmitter of COVID-19
A lot of media outlets and companies falsely informed that cash is a major infection channel for the COVID-19 virus, some claiming the World Health Organization (WHO) issued a warning regarding the use of cash, thus suggesting people should switch to cards and other cashless payment methods. This led to consumers being concerned about using cash and thus pushed more people to pay electronically. Let’s take a closer look:
- The WHO never issued any warning regarding the use of cash. “WHO did NOT say banknotes would transmit COVID-19, nor have we issued any warnings or statements about this,” said WHO spokeswoman Fadela Chaib in an email to MarketWatch (8).
- Germany’s Robert Koch Institute (RKI) for infectious diseases noted that handling banknotes does not pose a particular risk of contracting coronavirus (9).
- In its recent bulletin, the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) shared: “…scientists note that the probability of transmission via banknotes is low when compared with other frequently-touched objects. To date, there are no known cases of Covid-19 transmission via banknotes or coins.” In fact, research seems to suggest that the virus survives longer on card terminals and credit/debit cards as being shown for example in the graph below (10).
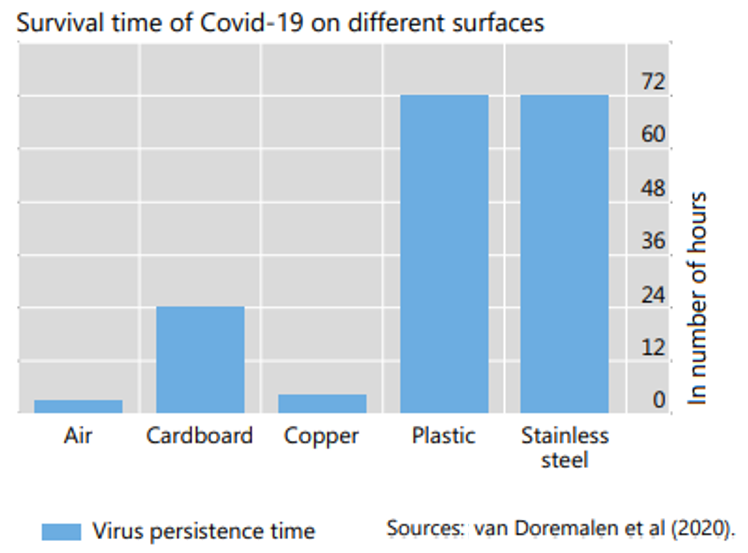
Bottom line: Cash is not an infection channel for COVID-19, there are many everyday-objects including cards with a higher probability to contain the COVID-19 virus. If you still feel afraid, then your ideal way to pay during the pandemic would be with contactless payment methods – however, you should still wash your hands.
How did COVID-19 affect other payment methods?
Just like cash, also card transactions saw a decrease in overall volume. Let’s not forget that generally, consumer spending is down globally across most industries (11), so naturally, this does not only have an effect on cash usage. Hence, even the two largest payment card networks Visa and Mastercard saw their transaction volume decline due to the coronavirus crisis (12, 13). On the positive side, they are witnessing more adoption for contactless or card-not-present transactions. According to a financial analysis by CO-OP Financial Services in the U.S., card-present transactions were down 41% in April 2020 compared to the previous year, however, card-not-present transactions increased by 30% during the same period (14). With that, the global mobile payments industry is set to see a jump of almost 50% in value amid the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, according to data by BuyShares (15). Without a doubt, there will be a shift in how consumers pay for their goods and certainly in favor of digital payments. But only until economies start to fully open up again and people start to spend in physical locations like restaurants, we will be able to get a clear picture of COVID-19’s long-term impact on the payments sector.
Cash demand increased globally amid COVID-19
Interestingly enough, while payments in cash have seen a decline during the pandemic, cash demand or cash-in-circulation has seen an increase in demand, globally. U.S. currency in circulation has experienced its largest percentage increase in over 20 years (16). The value of euro banknotes in circulation has increased by the largest amount since the 2008 financial crisis (17). Banco de Mexico reported cash circulating in the country reached the highest historical amount of 1.79 trillion Mexican pesos in the last week of April (18). The list goes on. These developments indicate that cash is still seen as an important ‘store of value’ and as a convenient and accessible way to pay in emergency situations.
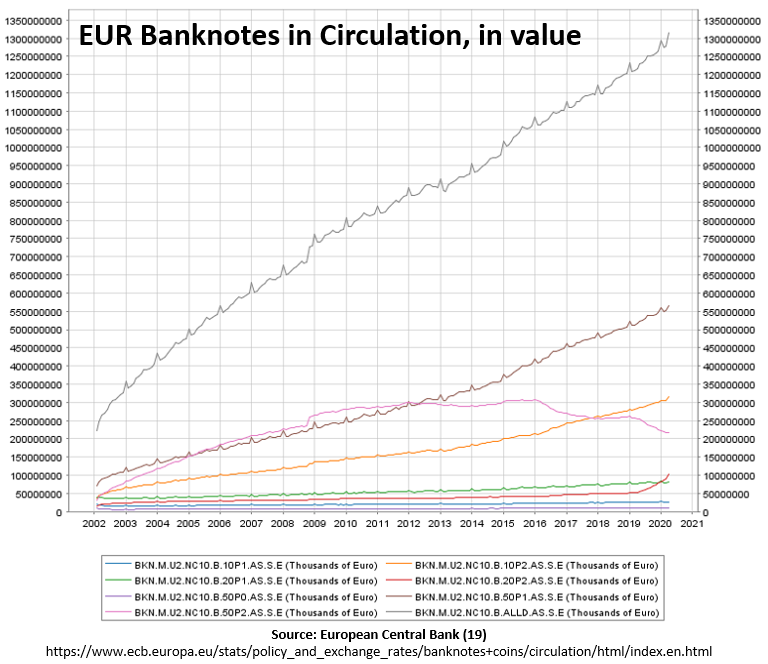
How popular was cash before the outbreak of the coronavirus?
Often I encounter that people, who are fortunate to live their everyday-life almost or totally cashless, thought cash was already about to die before this pandemic. Therefore, let’s also look at some additional facts regarding cash pre-COVID-19 (as mentioned above, how these statistics will be impacted due to the change in consumer behavior remains to be seen when economies fully open up again).
In most countries around the globe, cash remains the consumers’ preferred payment method. In Europe, about 80% of point-of-sale transactions are still made in cash (20). There are some outliers, most notably Sweden, which is often taken as an example for soon becoming the first cashless society, as in 2018 only 13% of its payments in physical stores were done in cash, according to the Riksbank (21). However, in the same year, Sweden experienced an increase in cash demand of 7% (22). It does not seem like this was due to a sudden shift in consumer behavior, nevertheless, there have been a lot of complaints to the government. Part of the population is not ready to shift to a digital society and others want to preserve their privacy, or simply want to keep their payment options open. Therefore the Riksdag adopted legislation in November 2019 to ensure access to cash services in the country (23). Other countries in Europe like Germany, Spain or Switzerland, still hold on to cash as their preferred payment method (24, 25, 26).
If we look at other regions, in Asia we have China which is moving rapidly to become even more digital. Thanks to solutions like Alipay and WeChat Pay, cash is no longer the preferred payment method. But just like in Sweden, there is criticism since a part of the population is not ready for a cashless society, especially in rural areas where many people do not have access to the internet or smartphones (27). In India, the government is pushing to move away from cash but the population is yet again not ready or not willing (28). Whereas Japan is another example of a developed economy holding on to the phrase ‘cash is king’ (29).
Lastly, let’s take a quick look at the Americas region. While in the U.S. cards are being used more, cash still enjoys an important role in the market and local regulators are even banning cashless stores and restaurants (30, 31). And well, Latin America clearly continues to be a cash stronghold. Even in the major FinTech hubs Mexico and Brazil (32), cash continues to account for most of the consumer payments with 90% and 71% respectively (33, 34). A common statement to justify the high share of cash in these markets is to attribute it to the unbanked population. A fair statement. However, if we look at adults in Mexico who have a bank account or a credit card, almost 80% of them continue to pay in cash (35), especially when it comes to payments of less than 500 Mexican Pesos (approx. 22.14 USD on the 22 of June 2020), as can be seen in the graph below (36).
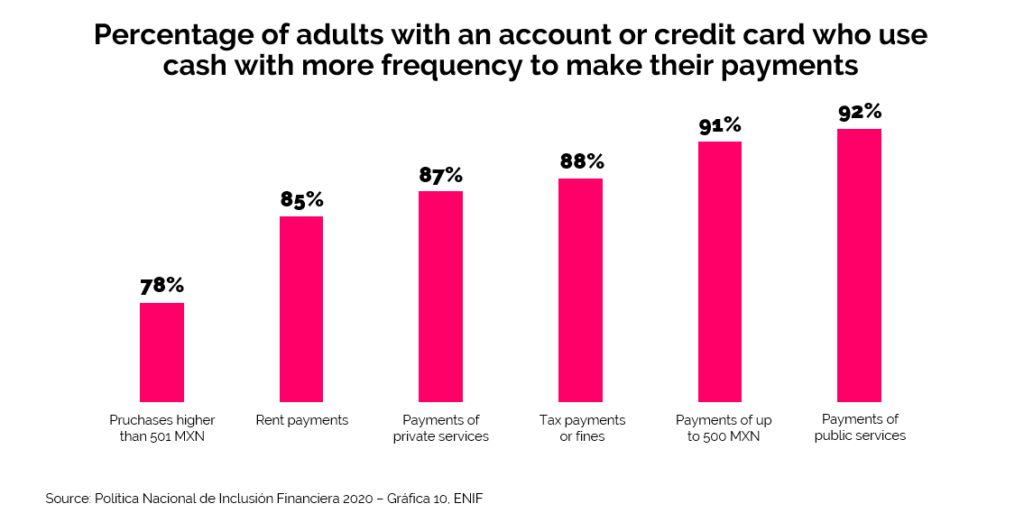
Cash will not be gone anytime soon
Again, the true long-term impact on the payments landscape can only be assessed as soon as economies start to operate ‘normally’ again. Nevertheless, the numbers show that cash continues to hold strong importance in our societies and that it will exist surely for a few more years or even decades. Some economies will make the leap to a cashless society earlier than others, but they will encounter the difficult task of providing access to cash to those excluded from the modern financial system. In my opinion, ‘the fight against cash’ is the wrong approach. We should rather strive to make access to financial services easier and include the financially excluded by giving consumers as many payment options as possible. If we solve this issue first and are able to successfully mitigate the risks of a cashless society, only then we are ready to live in a cashless world.
Hence, no, COVID-19 is not yet ‘the end’ of cash.
Disclaimer: I am an early employee and part of the management team at Sonect, a Swiss FinTech offering a fully-digital solution that turns any store into a virtual ATM. With Sonect, you can withdraw cash easily and safely using just your smartphone, wherever you are. At Sonect we aim to make access to financial services easier. Even though our business model revolves around cash, we aim to have an objective view when it comes to cash and can acknowledge both its pros and cons and with our solution we aim to help people and businesses transition from the cash economy to a digital future. My personal point-of-view regarding cash and digital payments: When I am in Switzerland I hardly use cash, in Mexico, on the other hand, I use it quite frequently. Generally, I prefer to pay digitally. However, neither do I take a stand for cash nor for cashless payments. In my opinion, what matters is consumer choice. People have different preferences, different needs, different lifestyles – so why should they not be able to choose from different payment methods and use what works best for them. Furthermore, I feel like in the push for the digital society, people in the fortunate position to experience the advantages of digital payments, often forget about the vast population that is still not ready to switch to digital payment methods. This creates the risk to exclude the financially excluded even more.
(1) https://news.shopify.com/shopify-announces-first-quarter-2020-financial-results (2) https://www.digitalcommerce360.com/article/quarterly-online-sales/ (3) https://www.reuters.com/article/health-coronavirus-swiss-delivery/swiss-farm-fresh-delivery-service-thrives-in-coronavirus-era-idUSL8N2BD2J4 (4) https://expansion.mx/tecnologia/2020/03/19/justo-la-app-para-pedir-el-super-en-linea-crece-330-por-el-coronavirus (5) https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-mexico-tally/confirmed-coronavirus-cases-in-mexico-rise-to-more-than-200-idUSKBN21801U (6) https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-03-18/europe-surpasses-china-in-number-of-confirmed-coronavirus-cases (7) https://www.jpmorgan.com/merchant-services/insights/reports/mexico (8) https://www.marketwatch.com/story/who-we-did-not-say-that-cash-was-transmitting-coronavirus-2020-03-06 (9) https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-germany-banknotes/banknotes-carry-no-particular-coronavirus-risk-german-disease-expert-idUSKBN20Y2ZT (10) https://www.bis.org/publ/bisbull03.pdf (11) https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/05/coronavirus-covid19-consumers-shopping-goods-economics-industry/ (12) https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-visa/visa-transaction-volumes-hurt-as-coronavirus-crisis-deepens-idUSKBN21H3DL (13) https://www.businessinsider.com/mastercard-sees-volume-slide-but-interest-in-contactless-rise-2020-4?r=MX&IR=T (14) https://www.cutimes.com/2020/05/13/analysis-transactions-drop-as-consumers-go-into-savings-mode-digital-payments-soar/ (15) https://thepaypers.com/mobile-payments/mobile-wallet-payments-to-surge-by-50-percent-in-2020–1242730 (16) https://www.coindesk.com/us-cash-in-circulation-sees-biggest-increase-since-the-y2k-bug-panic-fed-reserve-data-indicates (17) https://www.ft.com/content/28b59b28-44ac-43ec-b0dd-c1f1eacfbeb0 (18) https://www.forbes.com.mx/economia-finanzas-mexico-billetes-monedas-pandemia/ (19) https://www.ecb.europa.eu/stats/policy_and_exchange_rates/banknotes+coins/circulation/html/index.en.html (20) https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2020/649341/EPRS_BRI(2020)649341_EN.pdf (21) https://www.riksbank.se/en-gb/payments–cash/payments-in-sweden/payments-in-sweden-2019/the-payment-market-is-being-digitalised/cash-use-in-constant-decline/ (22) https://qz.com/1679019/swedens-cash-in-circulation-increased-for-the-first-time-since-2007/ (23) https://www.riksbank.se/en-gb/payments–cash/the-riksbanks-task-in-relation-to-payments/secure-access-to-cash—report-from-the-riksbank-committee/ (24) https://www.bundesbank.de/en/bundesbank/20-years-euro/cash-facts-and-figures-772080 (25) https://www.20minutos.es/noticia/3710698/0/dinero-efectivo-cash-tarjeta-credito-aproser/ (26) https://www.bbc.com/worklife/article/20190416-why-the-swiss-still-love-cash (27) https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Business-trends/In-China-cash-is-no-longer-king (28) https://www.reuters.com/article/us-india-demonetisation/love-of-cgash-hinders-indias-move-to-digital-economy-idUSKBN1XO05J?il=0 (29) https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2019/08/21/business/cash-king-aging-japan/ (30) https://www.pymnts.com/cash/2018/usa-global-cash-index-digital-dollar-cardtronics/ (31) https://edition.cnn.com/2020/01/23/us/nyc-cashless-ban/ (32) https://www.finnovista.com/en/radar/el-ecosistema-fintech-mexicano-recupera-el-liderazgo-en-america-latina-y-se-acerca-a-la-barrera-de-las-400-startups/ (33) https://www.pymnts.com/the-pymnts-com-global-cash-index-archives/ (34) https://valor.globo.com/financas/noticia/2019/10/04/para-71-dinheiro-e-principal-meio-de-pagamento.ghtml (35) https://www.afi-global.org/publications/3242/National-Financial-Inclusion-Strategy-Mexico (36) https://www.afi-global.org/publications/3242/National-Financial-Inclusion-Strategy-Mexico
Great article, I liked it very much congratulations!! 71126527
Your site is very good, I liked the information. Grateful. 24853072
Hi there! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to look it over.
I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be
tweeting this to my followers! Outstanding blog and superb design.